MVP & Lean Startup
MVP & Lean Startup
Startups are young companies that were founded to create a new product or service. These businesses usually aim to create new categories of goods and to change the way of thinking and leading business in all business sectors. There are plenty of cases when a startup completely changed the market. The founders are trying to give something that is needed but is not created yet. That’s why many startups fail and one of the main purposes is that a newly created service is ahead of time and potential customers do not understand the value of a new service.
Startups work like any other organization: a group of employees works on product creation that customers will buy. A completely understandable course of events, isn’t it? But the key difference is that classic businesses just duplicate what’s been done before, while startups’ main goal is to create a new template or even a business sector. So, the next conclusion follows: when the idea is new and there are no competitors, the founder has to do research and test the idea. Thus we came close to the question about MVP.
What MVP Is?
Minimal Viable Product (MVP) is a testable version of the product or service with a minimal set of functions. Nevertheless, MVP must be valuable for the customer. MVP is usually created for hypothesis testing and to check the product’s viability. The product testing results and customers’ feedback help to understand if the product is worth developing, what changes are needed to make, etc. The efficiency of building MVPs is proven by many huge companies, such as Spotify and Airbnb. The main aim of MVP is to reduce time and resource spending on idea testing.
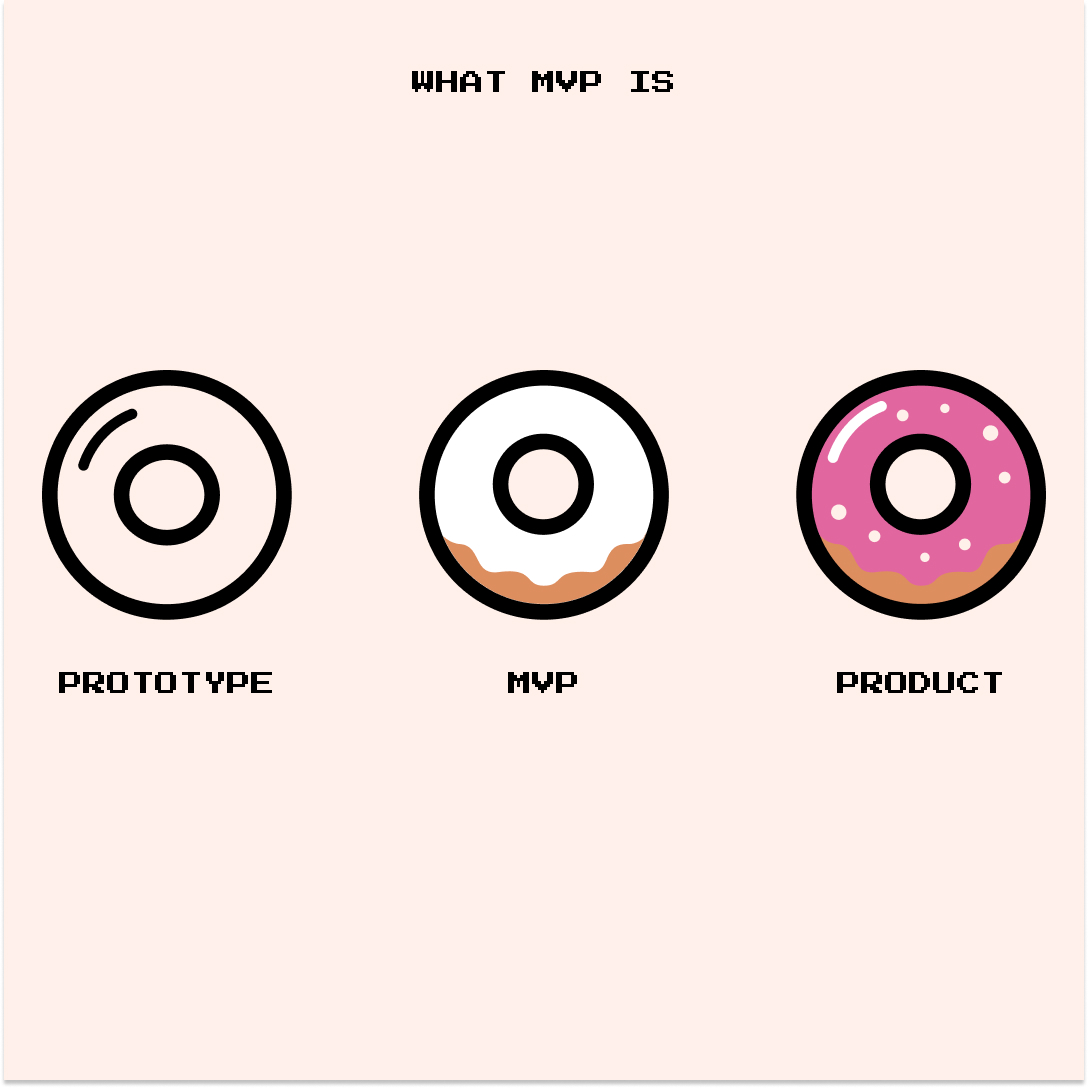
There are several types of MVPs and every type has its special features.
- Wizard of Oz MVP or Flintstoning MVP
The customer sees a full-fledged product, but in reality, it is only an imitation of an autonomous product, so every task is performed manually. If the manual testing gives good results, the founders usually start creating fully automated products. The selling of the “Flintstoning MVP” allows one to save funds and get clear indexes about the idea.- Concierge MVP
This method is more suitable for online services. The main aim of such services is to automate solving the problems of the target audience. The main difference between Concierge MVP and Wizard of Oz MVP is that there are no technologies here. Customers understand that they get the service from humans, not from a system.- Scattered MVP
The Scattered MVP is usually used when it is possible to test the idea without the software development. Instead of this founders try to collect already built tools and connect them into a single system. The development of unique solutions starts right after getting enough feedback and the first results.
What Lean Startup Is?
A lean startup is a set of practices that are used to deliver product value efficiently. The main difference between classic startups and lean startups is in the stages’ sequence. When an ordinary startup focuses on the product and only after the product is ready it begins to try to find a market, a lean startup has no focus on the product idea but on the market. After market research, a lean startup tries to find an idea for a product. The main idea of lean startups is to reduce spending on starting a business. It is like a business philosophy that allows us to save more resources.
Lean startups are always trying to add or change features of a product, so it will meet the users’ needs. That’s how the author of the Lean Startup idea describes the Lean Cycle:
- Ideas
- Build. The minimum amount of time spent building
- Product
- Measure
- Data
- Lean. Generate maximum amount of leaning
- Repeat the cycle from the very beginning
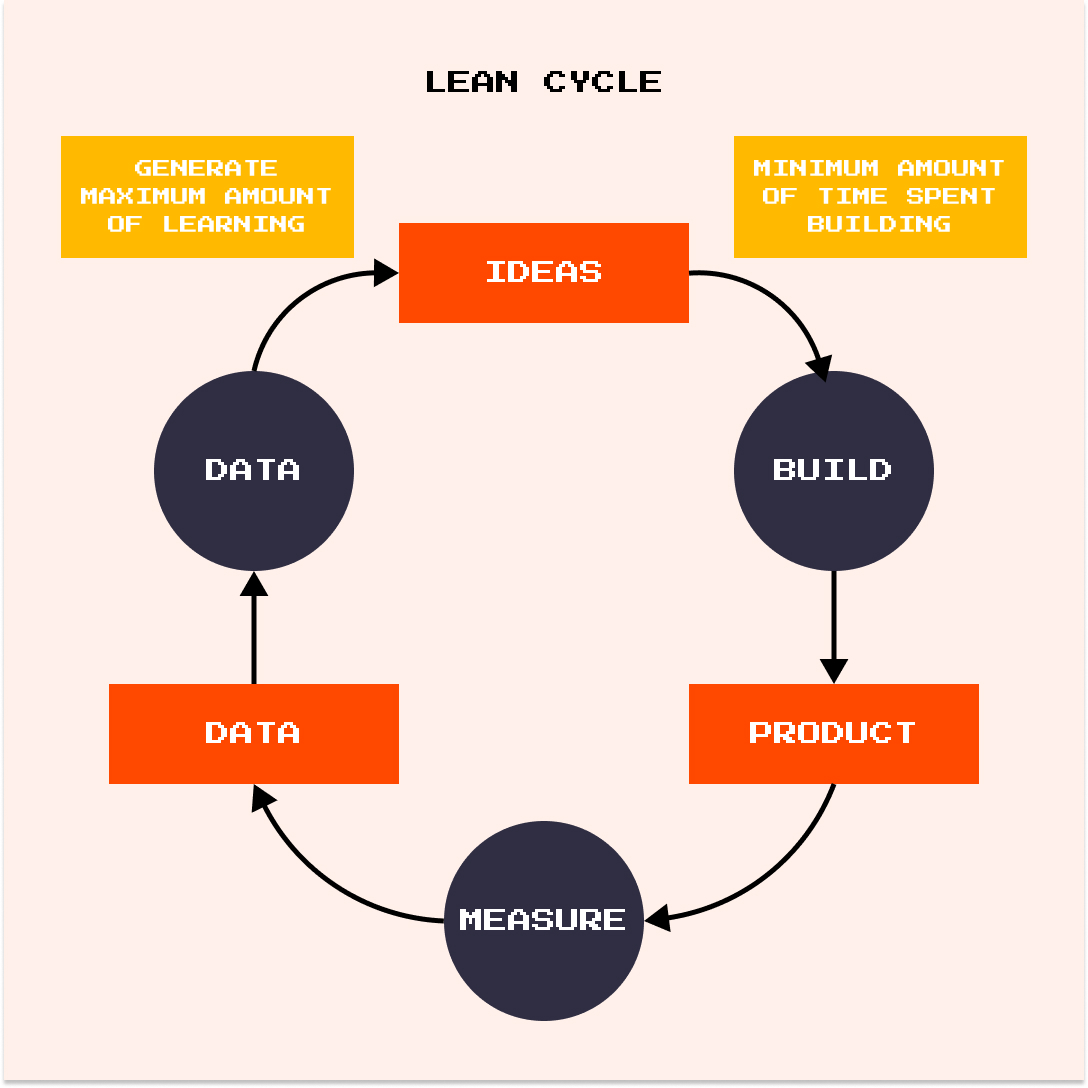
The main reason for using this cycle is to build a minimum amount of means as it gets built more quickly. That’s why the data measuring can begin much more quickly. So, we can see that MVP is a part of the Lean Startup idea. These are not different terms, but one concept (Lean Startup) includes another (MVP).
Summary. MVP Is a Part of a Lean Startup
In the beginning lean startups create a prototype of an idea - MVP. After that this prototype goes to potential clients and the founders begin to collect data and feedback about their prototype. At this point there are two ways: if there will be a specific number of users that indicate they would buy the product, the testing phase continues. If not - founders try to modify their MVP and find out how to make their product more desirable.




